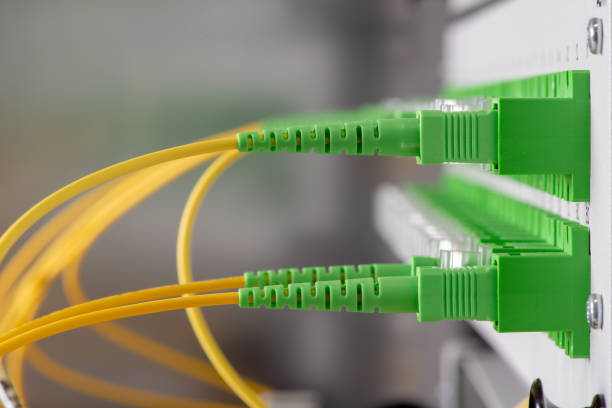
OS2 Singlemode Simplex and OS2 Singlemode Duplex are two common types of single-mode fiber optic cables, with core differences in fiber count, transmission direction, and application scenarios. Below is a clear, technical comparison:
1. Core Definition & Fiber Structure
| Feature | OS2 Singlemode Simplex | OS2 Singlemode Duplex |
| Fiber Count | 1 single-mode fiber core (OS2 standard: 9/125μm, low water peak, supports 1310nm/1550nm wavelengths) | 2 single-mode fiber cores (two independent 9/125μm OS2 fibers) |
| Physical Design | Single core + cladding + coating + jacket (no paired structure) | Two cores bundled in one jacket (often color-coded: e.g., blue/orange for differentiation) |
| Transmission Direction | Unidirectional (only one way for signal transmission) | Bidirectional (one core for Tx (transmit), one for Rx (receive)) |
2. Key Differences (Technical & Practical)
A. Transmission Capability
- Simplex: Only supports one-way data flow. For example, if you need to send data from Device A to Device B, you need a separate simplex cable to send data back from B to A (two simplex cables total for full duplex).
- Duplex: Native bidirectional transmission. The two cores work in pairs (Tx/Rx), enabling two-way communication with a single cable.
B. Connector Configuration
- Simplex: Uses single-fiber connectors (e.g., SC simplex, LC simplex) – only one ferrule (fiber core) in the connector.
- Duplex: Uses duplex connectors (e.g., SC duplex, LC duplex) – two ferrules side-by-side, pre-configured for Tx/Rx pairing (no need to manually match two simplex cables).
C. Installation & Cost
- Simplex: Lower cost per core, but requires two cables for full duplex (more wiring, higher installation labor).
- Duplex: Higher upfront cost than a single simplex cable, but reduces wiring complexity (one cable for two-way communication) – more cost-effective for bidirectional links.
D. OS2-Specific Advantage (Common to Both)
OS2 is a low-water-peak single-mode fiber (compatible with ITU-T G.652.D standard), supporting:
- Wavelengths: 1310nm (traditional) + 1550nm (long-haul) + 1625nm (testing/extended bands).
- Longer transmission distances (up to 10km for 1Gbps, 40km+ for 10Gbps with amplifiers) compared to multimode fiber (OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4).
- Lower attenuation (signal loss) – ideal for high-speed, long-distance applications.
3. Typical Application Scenarios
| Cable Type | Use Cases |
| OS2 Singlemode Simplex | – One-way signal transmission (e.g., security cameras, broadcast feeds). – Backup links or point-to-point unidirectional data streams. – Environments where bidirectional communication is not required. |
| OS2 Singlemode Duplex | – Bidirectional high-speed networks (e.g., data centers, enterprise LAN/WAN, 5G base stations). – Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) GPON/EPON networks (ONT to OLT links). – Long-haul connections between routers, switches, or servers (1Gbps/10Gbps/40Gbps/100Gbps). |
Summary of Core Differences
| Aspect | OS2 Simplex | OS2 Duplex |
| Fiber Cores | 1 (unidirectional) | 2 (bidirectional: Tx/Rx pair) |
| Communication Mode | One-way (full duplex needs 2 cables) | Two-way (single cable for full duplex) |
| Connector | Simplex (single ferrule) | Duplex (dual ferrule) |
| Best For | Unidirectional, low-cost links | Bidirectional, high-speed/long-haul networks |
In short: Choose OS2 Simplex for one-way transmission or cost-sensitive unidirectional links; choose OS2 Duplex for bidirectional, high-performance networks (the most common choice for modern fiber optic infrastructure).
 Câbles Cat5e
Câbles Cat5e Câbles Cat6
Câbles Cat6 Câbles Cat6a
Câbles Cat6a Câbles Cat8
Câbles Cat8 Câbles Ethernet en vrac
Câbles Ethernet en vrac Connecteurs et prises
Connecteurs et prises OS2 Singlemode Simplex
OS2 Singlemode Simplex OS2 Singlemode Duplex
OS2 Singlemode Duplex OM5 Multimode
OM5 Multimode OM4 Multimode
OM4 Multimode OM3 Multimode
OM3 Multimode OM2 Multimode
OM2 Multimode Câbles MTP/MPO
Câbles MTP/MPO Connectivité par fibre optique
Connectivité par fibre optique Câbles DisplayPort
Câbles DisplayPort Câbles Mini DisplayPort
Câbles Mini DisplayPort Câbles HDMI
Câbles HDMI Câbles mini/micro HDMI
Câbles mini/micro HDMI Câbles DVI
Câbles DVI Câbles VGA
Câbles VGA Câbles audio
Câbles audio Câbles Thunderbolt
Câbles Thunderbolt Câbles USB-C
Câbles USB-C Câbles USB 3.0
Câbles USB 3.0 Câbles d'alimentation
Câbles d'alimentation Câbles SATA
Câbles SATA Câbles série
Câbles série