Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | VGA | DVI |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Analog | Digital (some types also support Analog) |
| Image Quality | Lower, susceptible to interference and signal degradation | Higher, digital signal is lossless, resulting in a sharper image |
| Max Resolution | Theoretical 2048×1536, commonly 1920×1080 | Up to 2560×1600 (depending on type) |
| Video Support | Video Only | Video Only (DVI-I also carries VGA-compatible analog signal) |
| Audio Support | No | No |
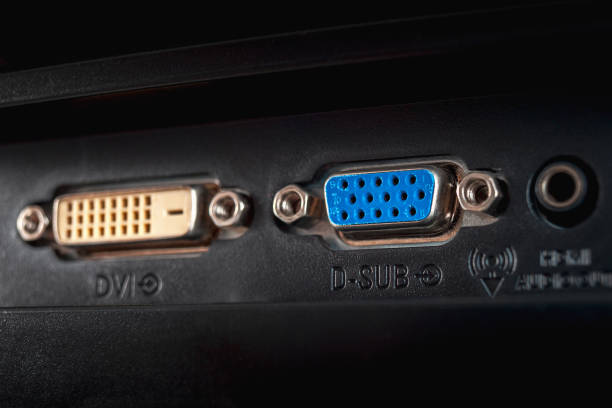
| Connector | 15-pin, D-Sub, usually blue | More pins, larger, with screw fixings |
| Status | Legacy, being phased out | Transitional standard, still common |
Detailed Explanation
1. Signal Type: Analog vs. Digital
This is the most fundamental difference.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array):
- How it works: The digital signal from the graphics card is converted to an analog signal for transmission over the cable. The monitor must then convert it back to digital for display on an LCD screen.
- Drawback: This “digital-to-analog-to-digital” conversion causes signal degradation. The analog signal is vulnerable to interference from other cables, resulting in a blurry, ghosted, or color-shifted image.
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface):
- How it works: The digital signal is sent directly from the source to the display without any conversion.
- Advantage: It provides a perfect, pixel-for-pixel image. As long as the cable is connected, the image is sharp and accurate, immune to analog noise.
2. Connector Types and Compatibility
The DVI connector has several variants, which is a common point of confusion:
- DVI-D (Digital Only): The most common type. Carries only a digital signal.
- DVI-I (Integrated): Carries both digital and analog signals. This allows for a simple passive adapter to convert a DVI-I port to VGA.
- DVI-A (Analog Only): Rarely used.
Crucial Note: You cannot use a simple passive adapter to connect a DVI-D (digital-only) port to a VGA monitor, as the necessary analog pins are missing. This requires an active converter.
3. Resolution and Use Cases
- VGA: Acceptable for 1080p and lower resolutions, but quality degrades significantly at higher resolutions (e.g., 1440p, 4K). Used for old computers, projectors, and some specialized equipment.
- DVI:
- Single Link: Supports up to 1920×1200 at 60Hz.
- Dual Link: Uses extra pins to support higher resolutions up to 2560×1600 at 60Hz. Essential for high-resolution monitors.
4. Modern Context & Recommendations
- VGA: Is an obsolete standard. New graphics cards and monitors rarely include VGA ports. Avoid it unless connecting very old equipment.
- DVI: Was a successful transitional standard, superior to VGA but now superseded by HDMI and DisplayPort. It is still very common on mainstream monitors and PCs.
- Pros: High-quality digital video, good enough for most office and general computing tasks.
- HDMI/DisplayPort: Are the modern standards. They support higher resolutions, refresh rates (e.g., 4K, 8K, high refresh rate gaming), and crucially, carry audio and other data.
Summary
- If both your devices have DVI, use DVI over VGA for a significantly clearer image.
- For connecting modern devices like game consoles, laptops, or for high-resolution/refresh-rate needs, use HDMI or DisplayPort.
- Adapters:
- DVI-I to VGA: Works (passive adapter).
- DVI-D to VGA: Does not work with a passive adapter; requires an active converter.
Simple Rule: Digital (DVI) is superior to Analog (VGA). Always prefer a digital connection when possible.
 Cables Cat5e
Cables Cat5e Cables Cat6
Cables Cat6 Cables Cat6a
Cables Cat6a Cables Cat8
Cables Cat8 Cables Ethernet a granel
Cables Ethernet a granel Conectores y tomas
Conectores y tomas OS2 Monomodo Simplex
OS2 Monomodo Simplex OS2 monomodo dúplex
OS2 monomodo dúplex OM5 multimodo
OM5 multimodo OM4 multimodo
OM4 multimodo OM3 multimodo
OM3 multimodo OM2 multimodo
OM2 multimodo Cables MTP/MPO
Cables MTP/MPO Conectividad de fibra óptica
Conectividad de fibra óptica Cables DisplayPort
Cables DisplayPort Cables Mini DisplayPort
Cables Mini DisplayPort Cables HDMI
Cables HDMI Cables HDMI Mini/Micro
Cables HDMI Mini/Micro Cables DVI
Cables DVI Cables VGA
Cables VGA Cables de audio
Cables de audio Cables Thunderbolt
Cables Thunderbolt Cables USB-C
Cables USB-C Cables USB 3.0
Cables USB 3.0 Cables de alimentación
Cables de alimentación Cables SATA
Cables SATA Cables serie
Cables serie