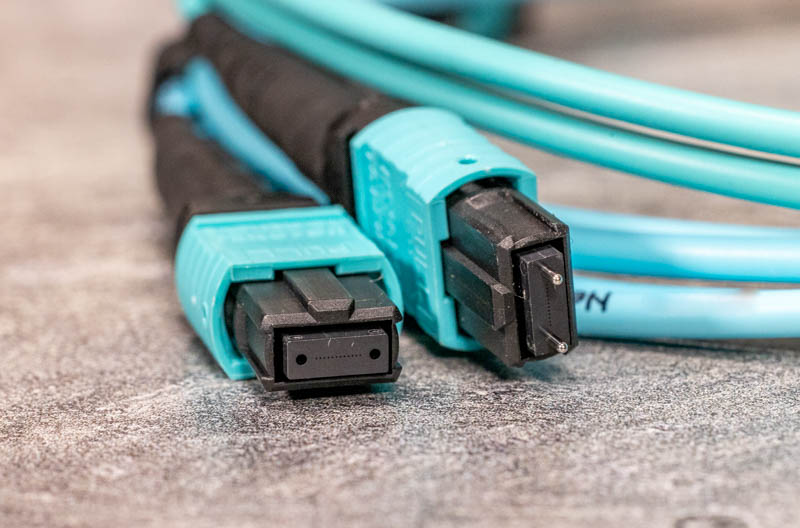
MTP optical cables are optimized and upgraded products with registered patents developed by Conec (USA) based on MPO optical cables. Both comply with international standards such as IEC 61754-7 and are interoperable. However, MTP has advantages in mechanical structure and optical performance, while MPO is widely used in conventional scenarios due to its standardization and cost-effectiveness. The detailed comparison is as follows:
1. Mechanical Structure
| Comparison Dimension | MPO Cables | MTP Cables |
| Pin Clip | Uses plastic pin clips. Pins are prone to breakage during frequent mating, resulting in poor durability. | Equipped with metal pin clips that firmly fix pins, significantly reducing the risk of accidental pin breakage during mating. Its elliptical spring increases the gap between the fiber ribbon and the spring, minimizing cable damage. |
| Ferrule Design | No floating ferrule. When subjected to external forces, the physical contact of paired fibers is easily affected, potentially leading to unstable connections. | Features an exclusive floating ferrule design. The ferrule can float inside the fiber, maintaining stable physical contact of paired fibers even under load, suitable for direct insertion into active Tx/Rx devices. |
| Guide Pin Characteristics | Adopts chamfered guide pins, which tend to generate debris during use. Debris accumulation can wear guide holes and affect transmission performance. | Uses stainless steel elliptical guide pins with small tolerances, reducing guide hole wear and the probability of debris falling into guide pin holes or ferrule endfaces, providing better protection for ferrules. |
| Housing Design | Non-detachable housing. If the ferrule malfunctions, rework and maintenance are difficult, and on-site polarity modification is not possible. | Detachable housing facilitates engineers to rework, polish, and perform performance testing on MT ferrules. It also allows flexible on-site polarity adjustment after assembly. Some enhanced MTP cables can quickly reconfigure fiber polarity. |
2. Optical Performance
Insertion Loss: MPO cables have relatively higher insertion loss, with ≤0.60dB for single-mode standard-precision products. Through precise component design and assembly processes, MTP achieves accurate alignment of male and female connectors, resulting in lower insertion loss—≤0.25dB for multi-mode high-precision products and ≤0.35dB for single-mode high-precision products—reducing signal loss during data transmission.
Stability and Durability: After 500 mating cycles, MPO cables show obvious damage to the endfaces near the guide holes. Signal fluctuations are likely to occur due to component wear during long-term use. In contrast, MTP cables maintain nearly intact guide hole endfaces after 600 mating cycles. Their optimized spring and guide pin designs reduce frictional damage between components, providing significantly better signal transmission stability and a longer service life than MPO.
3. Application Scenarios
MPO Cables: With standardized design and moderate cost, they are suitable for high-density cabling scenarios with general performance requirements. Typical applications include FTTX (Fiber to the X), basic connections for 40/100G SFP+ transceivers, and conventional fiber link deployment in small and medium-sized data centers. Common 8-24 core specifications meet basic bandwidth needs.
MTP Cables: Due to their excellent performance, they are more suitable for high-performance scenarios such as 400G Ethernet in super clouds, big data centers, and ultra-large-scale computing fields. They are also used for ultra-high-density cabling in large optical switches requiring high connection stability. Some enhanced MTP cables support rapid network configuration, meeting the needs of data center upgrades and flexible adjustments.
4. Market and Cost
MPO Cables: As universal standardized products, they have numerous manufacturers and sufficient market supply. Without patent-related additional costs, they offer more affordable overall prices and lower procurement and maintenance costs, making them a cost-effective choice for conventional cabling projects.
MTP Cables: Featuring patented technology, they require more complex production processes and higher material and assembly standards for core components, resulting in a higher price than ordinary MPO cables. However, for scenarios requiring high stability and later maintenance efficiency, this cost can be offset by reducing failure losses and lowering maintenance expenses.
 Cables Cat5e
Cables Cat5e Cables Cat6
Cables Cat6 Cables Cat6a
Cables Cat6a Cables Cat8
Cables Cat8 Cables Ethernet a granel
Cables Ethernet a granel Conectores y tomas
Conectores y tomas OS2 Monomodo Simplex
OS2 Monomodo Simplex OS2 monomodo dúplex
OS2 monomodo dúplex OM5 multimodo
OM5 multimodo OM4 multimodo
OM4 multimodo OM3 multimodo
OM3 multimodo OM2 multimodo
OM2 multimodo Cables MTP/MPO
Cables MTP/MPO Conectividad de fibra óptica
Conectividad de fibra óptica Cables DisplayPort
Cables DisplayPort Cables Mini DisplayPort
Cables Mini DisplayPort Cables HDMI
Cables HDMI Cables HDMI Mini/Micro
Cables HDMI Mini/Micro Cables DVI
Cables DVI Cables VGA
Cables VGA Cables de audio
Cables de audio Cables Thunderbolt
Cables Thunderbolt Cables USB-C
Cables USB-C Cables USB 3.0
Cables USB 3.0 Cables de alimentación
Cables de alimentación Cables SATA
Cables SATA Cables serie
Cables serie